1971. Find if Path Exists in Graph
leeetcode문제이고, 등급은 easy이다.
📖Description
There is a bi-directional graph with n vertices, where each vertex is labeled from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive). The edges in the graph are represented as a 2D integer array edges, where each edges[i] = [ui, vi] denotes a bi-directional edge between vertex ui and vertex vi. Every vertex pair is connected by at most one edge, and no vertex has an edge to itself.
You want to determine if there is a valid path that exists from vertex source to vertex destination.
Given edges and the integers n, source, and destination, return true if there is a valid path from source to destination, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
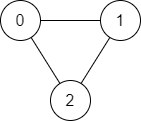
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0]], source = 0, destination = 2
Output: true
Explanation: There are two paths from vertex 0 to vertex 2:
- 0 → 1 → 2
- 0 → 2
Example 2:
1
2
3
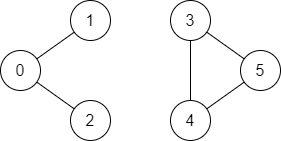
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,5],[5,4],[4,3]], source = 0, destination = 5
Output: false
Explanation: There is no path from vertex 0 to vertex 5.
bi_directional : 양쪽연결
시작점과 끝점 : u,v
Input : vertex의 개수, edges, source(시작지점), destination(목표지점)
output: source부터 destination까지 갈 길이 있는지 t/f 반환
🤔Intuition
- 엣지의 개수로는 연관성이 없다
- 노드가 있는지 확인
- source와 연결되어있는 vertex확인한다.
- 연결되어 있는 vertex가 destination이 아닌지 확인
- destination이 아니면 자신과 연결되어 있는 다른 vertex 확인
- 그게 destination인지 아닌지 판별한다.
- 위 과정을 반복한다.
이때 2번째 케이스의 경우, 0~1로 계속 반복해서 갈 수 있기 때문에 이것에 대한 종료조건이 필요하다.
🔍Approach
- bi-directional graph를 구현한다.
- 그래프 사이를 지나다니면서
- 그래프를 탐색하는 방법인 DFS와 BFS중에서 구현한다.
- Bi-directional 그래프를 만들어준다. 그래프를 만들어 엣지를 연결하는 것은 아래와 같은 코드를 이용하면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
dict = {} #빈 딕셔너리 선언
for i in range(n):
dict[i] = []
for i in edges:
dict[i[0]].append(i[1])
dict[i[1]].append(i[0])
- source, destination 연결 판단한다. 그러기 위해서 BFS를 사용한다. bfs는 리스트를 사용하여 append나 pop을 이용한다.
1
2
3
4
queue = [source]
# 큐에 뭐가 들어가야 하는걸까?
verify_list = queue
- 연결되어 있는 vertex가 destination인지 아닌지 확인하고 destination이라면 자신과 연결된 다른 vertex를 확인한다. 이 과정을 반복한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
while queue :
name = queue.pop(0)
if name == destination: #종료조건
return True
else:
for i in dict[name] :
if i in verify_list : # d가 verify_list에 있느냐를 의미
continue
queue.append(i)
verify_list.append(i)
return False #while문 끝나고 return
My submission
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
class Solution(object):
def validPath(self, n, edges, source, destination):
"""
:type n: int
:type edges: List[List[int]]
:type source: int
:type destination: int
:rtype: bool
"""
# 그래프 만들기
dict = {} #빈 딕셔너리 선언
for i in range(n):
dict[i] = []
for i in edges:
dict[i[0]].append(i[1])
dict[i[1]].append(i[0])
# source, destination 연결 판단 -> BFS 사용
queue = [source]
verify_list = queue
while queue :
name = queue.pop(0)
if name == destination: #종료조건
return True
else:
for i in dict[name] :
if i in verify_list : # d가 verify_list에 있느냐를 의미
continue
queue.append(i)
verify_list.append(i)
return False #while문 끝나고 return
- while로 무한 반복하는 것이 아니라 큐에 아무것도 없다면 반복을 종료한다. (
queue = []이 된다면False를 의미하기 때문에 멈춘다) - true를 반환하는 경우는 모든 엣지들이 연결되어 있는 경우이다. queue의 최상단을 꺼냈을 때, 목적지와 같다면 true를 반환하고 종료하면 된다. (
if queue.pop() == destination:) - 각각의 노드들을 봤는지 안 봤는지에 대한 코드가 필요하다. 만약 보지 않는다면 while문 안에서 계속 반복될 것이다. 따라서 위의 코드에서처럼 종료조건을 넣어주어야 한다.
내 코드는 런타임에러가 날 뿐만 아니라 외계인코드이다. 나도 그렇고 다른 사람도 그렇고 이해하기 어렵다. 따라서 스터디를 진행한 선배의 코드와 leetcode 공식 코드를 추가적으로 첨부한다.
Others Submission
- source와 연결되있는 node에 접근한다.
- node의 값이 destination과 같은지 확인한다.
- 현재 node를 source로 하고 여기에 연결되있는 node에 접근한다.
- node의 값이 destination과 같은지 확인 반복한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
class Solution:
def validPath(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int) -> bool:
"""
1. source와 연결되있는 node에 접근
2. node의 값이 destination과 같은지 확인
3. 현 node를 source로 하고 여기에 연결되있는 node에 접근
4. node의 값이 destination과 같은지 확인 반복
"""
graph = {}
seen = [False] * n
for i in range(n):
graph[i] = []
for u, v in edges:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
queue = [source]
while queue:
current = queue.pop(0)
if current == destination:
return True
for i in graph[current]:
if not seen[i]:
seen[i] = True
queue.append(i)
return False
Official Implementation : using BFS
official 코드를 보면 여러 구현 방식이 있으나 그 중에서 나와 중범선배의 코드와 흐름이 같은 BFS를 사용한 코드를 가져왔다.
- 방문한 노드를 저장하기 위한 대기열인 빈 큐 (
queue)를 초기화한다. - 이미 방문한 노드를 표시할 bool형 배열인
seen을 생성하고, 모든 노드를 저장할 hash mapgraph를 만든다. - Queue의 시작 노드인 source를 추가하고 seen에 방문한 것을 업데이트한다.
queue에 노드가 있으면queue에서 현재 노드(curr_node)를 가져온다. 그 다음 현재 노드(curr_node)가destination인지 판별한다.destination이면true를 반환하고, 아니면 5단계로 이동한다.- 아직 방문하지 않은 이웃노드는
queue에 추가하고, 그들이 방문했다는 것을 표시한다. 이후, 4단계를 반복한다. destination을 찾는 것 없이queue가 비게 되면 비워지게 되면false를 반환한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
class Solution:
def validPath(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int) -> bool:
# Store all edges in 'graph'.
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
for a, b in edges:
graph[a].append(b)
graph[b].append(a)
# Store all the nodes to be visited in 'queue'.
seen = [False] * n
seen[source] = True
queue = collections.deque([source])
while queue:
curr_node = queue.popleft()
if curr_node == destination:
return True
# For all the neighbors of the current node, if we haven't visit it before,
# add it to 'queue' and mark it as visited.
for next_node in graph[curr_node]:
if not seen[next_node]:
seen[next_node] = True
queue.append(next_node)
return False
💡Remembrance
- 그래프에 대해 아무것도 몰랐으나, 이 문제를 스터디를 통해 고민하고 구현해보면서 그래프와 bi-directional graph에 대해 이해할 수 있었다.
- bfs와 dfs를 각각은 알았지만 이를 그래프 탐색에 사용되는 방법으로써는 처음 사용해본 것 같다. 이론을 할 때는 십게 이해했지만 막상 그래프를 탐색할 때는 bfs와 dfs가 빠르게 떠오르지 않았다. 이렇게 새로 배워간다!
- 솔직히 시간을 많이 투자했음에도 이해가 잘 되지 않는다. 스터디가 끝나면 바로바로 정리해야겠다. 또 다음에 한 번 더 복습하러 와야겠다.